Blobs
Only applicable after the Deneb/Cancun Hardfork
Blobs are stored locally as data column sidecars post Fusaka Hardfork
Background
EIP-4844 aka proto-danksharding in the Deneb/Cancun hardfork brings a data availability layer to Ethereum that allows for temporary storage of arbitrary data on the blockchain. The arbitrary data stored in this way are called blobs and there can be 3 ~ 6 blob sidecars (an object wrapper for blobs) associated to each block. This EIP marks ethereum's first steps towards sharding and scalability by allowing L2s to leverage this DA layer to reduce gas fees for their users and allowing for more transitions to be processed.
EIP-7691: Blob throughput increase is a post Electra hardfork EIP that increases the target number of blobs from 3 to 6 and max number of blobs from 6 to 9.
One design decision in the implementation of EIP-4844 to verify blobs and to enable the future path of proposer-builder separation is the use of KZG commitments. In order to use KZG commitments a Trusted Setup is needed. For the Deneb hardfork a KZG Ceremony was conducted to create the Trusted Setup. For technical awareness, Prysm loads the Trusted Setup from prysm/beacon-chain/blockchain/kzg/trusted_setup.json
Post Fusaka
EIP-7594 PeerDAS (Peer Data Availability Sampling) is a networking protocol that allows nodes to perform data availability sampling (DAS) to ensure that blob data is available while downloading only a subset of the data. The number of data columns you custody will depend on the number of validators attached to your beacon node.
EIP-7892 BPO (blob parameter only) hardforks that increase the max blob count
| Time | Epoch | Max Blobs |
|---|---|---|
| December 9, 2025, 02:21:11pm UTC | 412672 | 15 |
| January 7, 2026, 01:01:11am UTC | 419072 | 21 |
Storage Requirements:
Post Fusaka Hardfork, custody requirements will be dependent on the number of validators you run with and whether you use the --subscribe-all-data-subnets flag, converting your node into a super node.
For detailed estimates on requirements, please visit fusaka-bandwidth-estimation by the Ethereum Foundation Devops Team.
The most significant impact on node operators is the increased storage requirement. Node runners have a new slightly increased storage requirement
Example from electra hardfork:
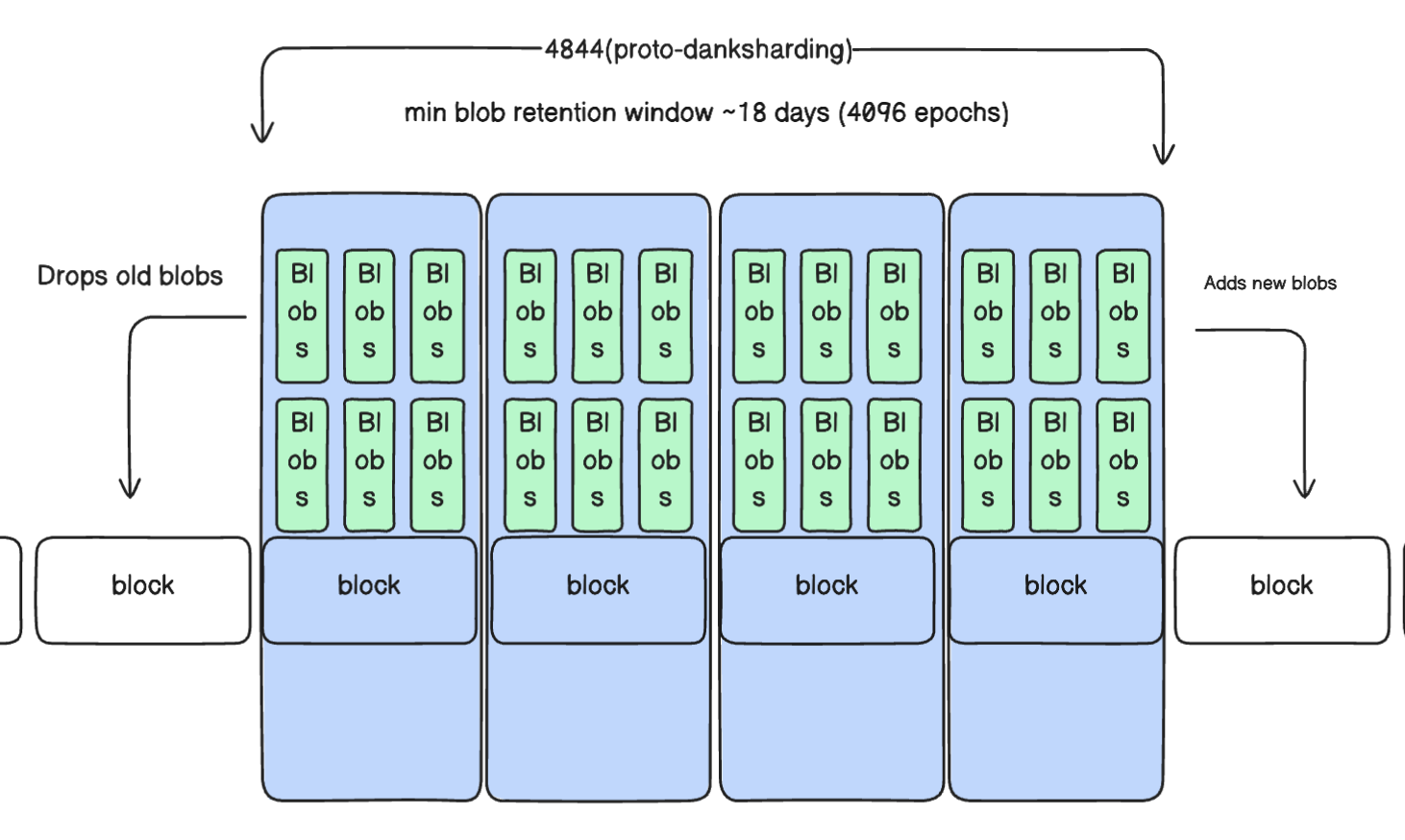
131928 blob ssz byte size * blobs retention period (18 days or 4,096 epochs) * 32 potential blocks per epoch * 6~9 Blob sidecars per block
= 100GB~150GB
By default these blobs will be retained for 4096 epochs, and Prysm will prune the oldest blobs once the retention period is reached.
Retention periods and storage paths can be configured using the following flags.
Network Requirements (Post Fusaka):
PeerDAS in the Fusaka hardfork introduces new data column requirements, including a new way to distribute blobs across the network. Networking requirements will also depend on the BPO we are on and the number of max blobs Ethereum supports.
For detailed estimates on requirements, please visit fusaka-bandwidth-estimation by the Ethereum Foundation Devops Team.
Flags
--blob-path: Location for blob storage. The default location will be a 'blobs' directory next to the beacon DB. i.e.,--data-dir=/path/to/storage--blob-retention-epochs: Override the default blob retention period (measured in epochs). The node will exit with an error at startup if the value is less than the default of 4096 epochs. i.e.,--blob-retention-epochs=6000. This flag is usable for Data columns post-Fusaka.--supernode: Converts your node into aSuper nodewhich custodies all data columns regardless of the number of connected validators to the node. Use this flag if you need to retrieve blobs regularly. Note: The original flag namesubscribe-all-data-subnetsis aliased. Warning: Significantly increases hardware and networking requirements.--semi-supernode: Custodies just enough data to serve the blobs and blob sidecars beacon API. This mode custodies the minimum number of data columns required for reconstruction (typically half of all columns, e.g., 64 out of 128), providing a middle ground between normal operation and full supernode mode, allowing blob reconstruction while using less storage and bandwidth than a full supernode. Warning: Cannot be used with--supernode.